

| Esophageal Dilation |
What is Esophageal Dilation?
Esophageal dilation is a procedure that allows your doctor to dilate, or stretch, a narrowed area of your esophagus [swallowing tube]. Doctors can use various techniques for this procedure. Your doctor might perform the procedure as part of a sedated endoscopy. Alternatively, your doctor might apply a local anesthetic spray to the back of your throat and then pass a weighted dilator through your mouth and into your esophagus.
Why is it Done?
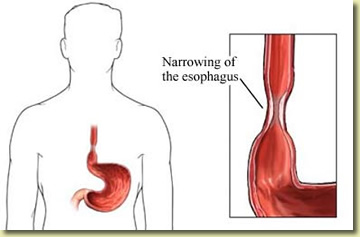
The most common cause of narrowing of the esophagus, or stricture, is scarring of the esophagus from reflux of acid occurring in patients with heartburn. Patients with a narrowed portion of the esophagus often have trouble swallowing; food feels like it is "stuck" in the chest region, causing discomfort or pain. Less common causes of esophageal narrowing are webs or rings (which are thin layers of excess tissue), cancer of the esophagus, scarring after radiation treatment or a disorder of the way the esophagus moves [motility disorder].
How Should I Prepare for the Procedure?
An empty stomach allows for the best and safest examination, so you should have nothing to drink, including water, for at least 4 - 6 hours before the examination. Your doctor will tell you when to start fasting.
Tell your doctor in advance about any medications you take, particularly aspirin products or anticoagulants (blood thinners). Most medications can be continued as usual, but you might need to adjust your usual dose before the examination. Your doctor will give you specific guidance. Tell your doctor if you have any allergies to medications as well as medical conditions such as heart or lung disease. Also, tell your doctor if you require antibiotics prior to dental procedures, because you might need antibiotics prior to esophageal dilation as well.
What Can I Expect during Esophageal Dilation?
Your doctor might perform esophageal dilation with sedation along with an upper endoscopy. Your doctor may spray your throat with a local anesthetic spray, and then give you sedatives to help you relax. Your doctor then will pass the endoscope through your mouth and into the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
The endoscope does not interfere with your breathing. At this point your doctor will determine whether to use a dilating balloon or plastic dilators over a guiding wire to stretch your esophagus. You might experience mild pressure in the back of your throat or in your chest during the procedure. Alternatively, your doctor might start by spraying your throat with a local anesthetic. Your doctor will then pass a tapered dilating instrument through your mouth and guide it into the esophagus.
What Can I Expect after Esophageal Dilation?
After the dilation is done, you will be observed for a short period of time and then your physician will provide discharge instructions on resuming activities and diet. Most patients experience no symptoms after this procedure and can resume eating the next day, but you might experience a mild sore throat for the remainder of the day.
If you received sedatives, you probably will be monitored in a recovery area until you are ready to leave. You will not be allowed to drive after the procedure even though you might not feel tired. You should arrange for someone to accompany you home, because the sedatives might affect your judgment and reflexes for the rest of the day.
Will Repeat Dilations be Necessary?
Depending on the degree of narrowing of your esophagus and its cause, it is common to require repeat dilations. This allows the dilation to be performed gradually and decreases the risks of the procedure. Once the stricture, or narrowed esophagus, is completely dilated, repeat dilations may not be required. If the stricture was due to acid reflux, acid-suppressing medicines can decrease the risk of stricture recurrence.