

| Anorectal Manometry |
Anorectal manometry is a test performed to evaluate patients with constipation or fecal incontinence. This test measures the pressures of the anal sphincter muscles, the sensation in the rectum, and the neural reflexes that are needed for normal bowel movements.
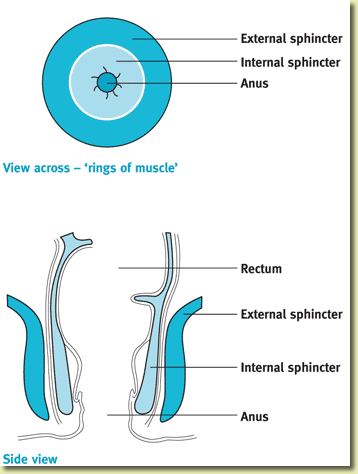
How is the Test Performed
The test takes approximately 30 minutes. You will be asked to change into a hospital gown. A technician or nurse will explain the procedure to you, take a brief health history, and answer any questions you may have. The patient then lies on his or her left side. A small, flexible tube, about the size of a thermometer, with a balloon at the end is inserted into the rectum. The catheter is connected to a machine that measures the pressure. During the test, the small balloon attached to the catheter may be inflated in the rectum to assess the normal reflex pathways. The nurse or technician may also ask the person to squeeze, relax, and push at various times. The anal sphincter muscle pressures are measured during each of these maneuvers. To squeeze, the patient tightens the sphincter muscles as if trying to prevent anything from coming out. To push or bear down, the patient strains down as if trying to have a bowel movement.
What can be learned from anorectal manometry?
The anal and rectal area contains specialized muscles that are helpful to regulate proper passage of bowel movements. Normally, when stool enters the rectum, the anal sphincter muscle tightens to prevent passage of stool at an inconvenient time. If this muscle is weak or does not contract in a timely way, incontinence (leakage of stool) may occur. Normally, when a person pushes or bears down to have a bowel movement, the anal sphincter muscles relax. This will cause the pressures to decrease allowing evacuation of stool. If the sphincter muscles tighten when pushing, this could contribute to constipation.
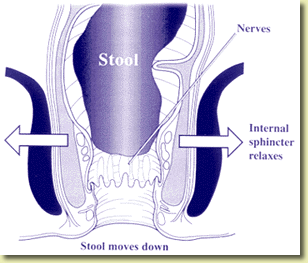
Anal manometry measures how strong the sphincter muscles are and whether they relax as they should during passing a stool. It provides helpful information to the doctor in treating patients with fecal incontinence or severe constipation.
There are many causes of fecal incontinence. Weak anal sphincter muscles or poor sensation in the rectum can contribute to fecal incontinence. If these abnormalities are present, they can be treated. Biofeedback techniques using anal manometry and special exercises of the pelvic floor muscles can strengthen the muscles and improve sensation. This can help treat fecal incontinence.
There are many causes of constipation. Some involve sluggish movement through the whole colon, whereas others involve the anal sphincter muscles. In some patients with constipation, the anal sphincter muscles do not relax appropriately when bearing down or pushing to have a bowel movement. This abnormal muscle function may cause a functional type of obstruction. Muscles that do not relax with bearing down can be retrained with biofeedback techniques using anal manometry.