

| Screening For Colorectal Cancer |
Screening
Screening tests help your doctor find polyps or cancer before you have symptoms. Finding and removing polyps may prevent colorectal cancer. Also, treatment for colorectal cancer is more likely to be effective when the disease is found early.
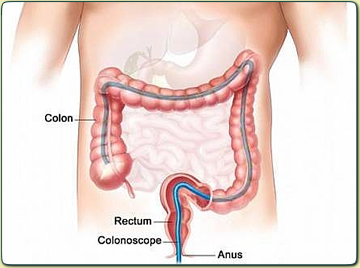
To find polyps or early colorectal cancer:
People in their 50s and older should be screened.
People who are at higher-than-average risk of colorectal cancer should talk with their doctor about whether to have screening tests before age 50, what tests to have, the benefits and risks of each test, and how often to schedule appointments.
The following screening tests can be used to detect polyps, cancer, or other abnormal areas. Your doctor can explain more about each test:
Fecal occult blood test (FOBT): Sometimes cancers or polyps bleed, and the FOBT can detect tiny amounts of blood in the stool. If this test detects blood, other tests are needed to find the source of the blood. Benign conditions (such as hemorrhoids) also can cause blood in the stool.
Sigmoidoscopy: Your doctor checks inside your rectum and the lower part of the colon with a lighted tube called a sigmoidoscope. If polyps are found, the doctor removes them. The procedure to remove polyps is called a polypectomy.
Colonoscopy: Your doctor examines inside the rectum and entire colon using a long, lighted tube called a colonoscope. Your doctor removes polyps that may be found.
Double-contrast barium enema: You are given an enema with a barium solution, and air is pumped into your rectum. Several x-ray pictures are taken of your colon and rectum. The barium and air help your colon and rectum show up on the pictures. Polyps or tumors may show up.
In the United States, colorectal cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, after skin, prostate, and lung cancer. It is also the fourth most common cancer in women, after skin, breast, and lung cancer.
Screening For Colorectal Cancer |
Symptoms
A common symptom of colorectal cancer is a change in bowel habits. Symptoms include:
Having diarrhea or constipation
Feeling that your bowel does not empty completely
Finding blood (either bright red or very dark) in your stool
Finding your stools are narrower than usual
Frequently having gas pains or cramps, or feeling full or bloated
Losing weight with no known reason
Feeling very tired all the time
Having nausea or vomiting
Most often, these symptoms are not due to cancer. Other health problems can cause the same symptoms. Anyone with these symptoms should see a doctor to be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Usually, early cancer does not cause pain. It is important not to wait to feel pain before seeing a doctor.
Download This National Cancer Institute booklet about cancer of the colon and rectum by clicking the image below.